CNC Machining for Modern Medical Manufacturing
Understanding What CNC Machining Is
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining refers to a digitally controlled manufacturing method where programmed instructions guide automated machines to precisely cut, mill, drill and shape components. This technology can process a wide range of materials including metals such as aluminum, titanium and stainless steel, as well as plastics and composites.
CNC machining includes various processes—milling, turning, cutting, grinding, drilling and polishing—all operating from pre-set programs to maintain exceptional consistency, repeatability and accuracy. Its efficiency minimizes waste, setup time and manual intervention, making it ideal for both high-volume production and custom CNC parts.
Today’s advanced CNC systems feature multi-axis machining, automated tool changers and strong automation capabilities. These features significantly improve production efficiency and enable manufacturers like Xstar to deliver tight-tolerance components quickly and reliably.
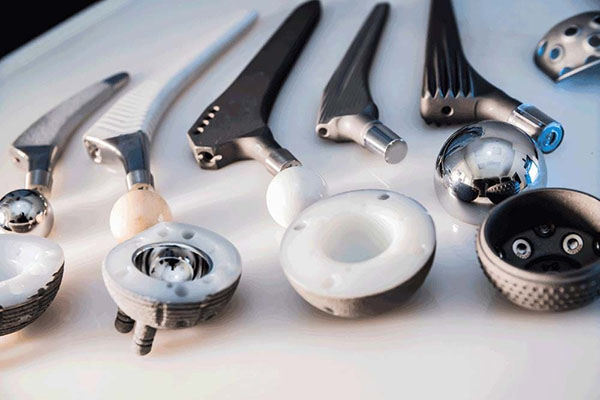

Why CNC Machining Is Essential in the Medical Sector
The adaptability and precision of CNC machining in the medical sector have transformed how medical devices are designed, manufactured and customized. The ability to achieve high accuracy, produce patient-specific components and develop complex structures supports innovation across prosthetics, implants and surgical instruments, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Below are the core advantages of integrating CNC medical machining into healthcare device production.
Precision and Accuracy in Medical CNC Production
Medical-grade devices must meet extremely tight tolerances, and CNC machines are capable of delivering the ultra-precise geometry required for implants, micro-devices and surgical tools. Doctors rely on instruments that perform consistently during critical procedures, and CNC machining enables the creation of highly dependable surgical components—from scalpel handles to robotic-assisted surgical parts.
By maintaining consistency across batches, medical CNC machining significantly reduces performance risks and improves the safety of surgical operations.

Customization and Personalization for Patient-Specific Devices
Healthcare increasingly depends on personalized solutions, and CNC machining medical parts plays a central role in this shift. Using data derived from CT scans, MRI images or 3D body scans, CNC machines can fabricate patient-specific implants, dental prosthetics, hearing aid components and orthopedic devices.
These tailored parts improve comfort, functionality and surgical outcomes while helping patients recover faster. The capability to produce one-off or small-batch custom components makes CNC machining a cornerstone of modern medical precision manufacturing.
Ability to Produce Complex Structures
CNC machining excels at creating intricate shapes and internal geometries that traditional methods struggle to achieve. Cavities, channels and detailed internal features required in high-performance implants or micro-devices can be machined with exceptional accuracy.
This strength allows CNC machining medical parts to meet the growing demand for miniaturization and advanced medical engineering.
Rapid Prototyping for Faster Innovation
By combining CAD software with CNC automation, medical engineers can quickly turn digital concepts into functional prototypes. This accelerates design testing, improves iterative development and shortens the timeline for regulatory-ready medical devices.
Rapid prototyping helps healthcare manufacturers evaluate functionality, refine ergonomics and validate performance before committing to mass production—resulting in faster and safer delivery of new medical technologies.
Process Optimization Through Automation and AI
The integration of CNC machining with automation, smart monitoring and AI-assisted systems has improved consistency and minimized human error across production lines. Automated CNC systems can operate continuously, switch rapidly between part types and machine several surfaces in a single setup.
This leads to:
-
Shorter production cycles
-
Reduced downtime
-
Higher output efficiency
-
Lower defect rates
Such advancements enhance both the reliability and scalability of medical CNC machining.
Wide Material Compatibility for Medical Applications
CNC machining supports numerous biocompatible and durable materials, including titanium, stainless steel, medical-grade plastics and high-performance composites. This flexibility allows manufacturers to balance strength, biocompatibility, weight and cost when developing critical medical components.
Cost-Efficiency and Long-Term Savings
Despite the initial investment, CNC machining reduces overall manufacturing expenses by cutting material waste, eliminating custom fixtures and minimizing setup time. In medical manufacturing—where materials like titanium and platinum are extremely valuable—CNC machining significantly lowers cost through optimized material usage.
Key Medical Applications of CNC Machining
Surgical Tools
CNC machining is widely used to manufacture surgical instruments that require high precision and durability. Tools such as scalpels, forceps, clamps and retractors can be made to exact specifications to ensure consistent performance and reliability during use.
Implants
Orthopedic, spinal and dental implants require extremely accurate dimensions to ensure stability and compatibility within the body. CNC machining enables the production of custom implants using biocompatible materials, improving patient comfort and long-term success rates.
Prosthetics and Orthotics
With CNC machining, patient-specific prosthetic limbs and orthotic devices can be crafted using accurate digital scan data. These custom components provide improved comfort, better mobility and enhanced quality of life for individuals with physical impairments.
Microdevices for Advanced Medical Systems
CNC machining also supports the fabrication of highly detailed microdevices, which are essential for modern diagnostics and drug delivery systems. These components often require extremely tight tolerances and complex micro-geometries that only precision CNC methods can achieve. From biosensors to microfluidic channels, CNC machining enables accurate and repeatable production that fuels next-generation medical innovation.
Medical Device Enclosures and Housings
Many diagnostic devices, monitoring systems and portable healthcare instruments use CNC-machined housings to protect sensitive internal components. These enclosures must provide exceptional structural stability, smooth interfaces and precise fitment. CNC machining ensures each part meets the demanding standards required in the medical CNC machining field.
Diagnostic Equipment Components
CNC machining contributes significantly to the manufacturing of parts for MRI machines, CT scanners, laboratory analyzers and point-of-care diagnostic tools. These complex systems depend on reliable, high-precision components that support accurate measurement and performance during testing and imaging.
Instruments for Minimally Invasive Surgery
Laparoscopic and endoscopic procedures require tools with extremely fine details, ergonomic design and reliable structure. CNC machining provides the accuracy needed to produce such instruments, supporting minimally invasive techniques that result in reduced patient trauma and faster recovery times.
Rehabilitation and Assistive Devices
Customized rehabilitation devices, such as braces, supports and mobility aids, rely heavily on CNC machining to achieve optimal fit and performance. By tailoring components to individual patient needs, manufacturers can improve comfort, functionality and overall user experience.
Limitations of CNC Machining in the Medical Sector
Geometric Complexity Constraints
Although CNC machining can produce moderately complex geometries, certain extreme shapes—such as deep internal cavities, significant undercuts or inaccessible internal details—may require specialized tooling or additional operations. These extra steps can add cost and time to the production process.
Material Limitations
While CNC machining supports biocompatible materials like titanium, aluminum and high-performance plastics, certain ceramics or heat-sensitive polymers are more challenging to machine. These materials may deform under heat or require unique tooling setups, affecting production speed and accuracy.
Production Speed Considerations
For highly complex parts, CNC machining may take longer than alternative manufacturing technologies, especially for mass-production environments. This can affect the overall lead time required to meet large-scale medical demand.
Size Restrictions
The size of a CNC machine determines the maximum dimensions of the parts it can produce. Large or oversized medical components may not fit within standard CNC work envelopes, requiring different manufacturing techniques.
Surface Finish Requirements
Some medical components require extremely smooth finishes or specific texture profiles for optimal performance or biocompatibility. While CNC machining provides excellent precision, additional finishing steps such as polishing or coating may be necessary.
Need for Skilled Operators
Although automation is increasing, CNC machining still requires trained professionals capable of programming, monitoring and maintaining equipment. A shortage of skilled operators in many regions can challenge the scalability of CNC machining in the medical sector.
The Future of CNC Machining in the Medical Field
Increased Automation and Digital Integration
Advances in robotics, AI and machine learning will continue enhancing CNC machining. Automated material handling, smarter tool selection and real-time quality monitoring will further improve production reliability. Integration with CAD/CAM and simulation tools will allow companies like Xstar to streamline workflows and accelerate product development.
Customization and Personalized Medicine
As patient-specific solutions become more common, CNC machining will remain essential for creating custom CNC machining medical parts. Combined with medical imaging and 3D scanning, CNC technology will enable more accurate and personalized implant designs, improving treatment outcomes.
Enhanced Regulatory Compliance
With growing regulatory requirements in the medical sector, CNC machining will continue evolving to support traceability, validation and complete documentation. This ensures consistent quality and compliance throughout production.
Miniaturization Advancements
The need for smaller, more advanced medical devices will strengthen the demand for micro-precision CNC machining. Ultra-small features, micro-channels and intricate shapes will support innovations in targeted drug delivery, minimally invasive tools and diagnostic systems.
New Material Capabilities
As material science continues advancing, CNC machining will adapt to new biocompatible, lightweight and high-strength materials. This will allow manufacturers to design safer and more efficient medical products.
Hybrid Manufacturing With 3D Printing
Combining CNC machining with additive manufacturing introduces powerful new capabilities. 3D printing provides design flexibility, while CNC machining delivers tight tolerance finishing. Together, they enable the creation of complex and optimized medical components with reduced processing time.
Need a Precision Medical Part Machined?
Get an instant quote today and discover how Xstar’s advanced CNC machining medical parts capabilities can support your next project.
